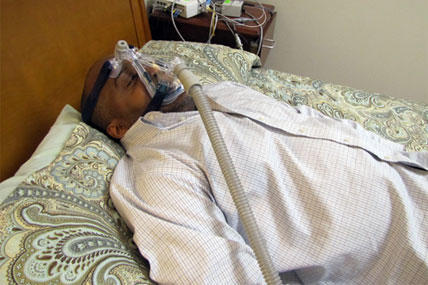
Last June the VA Advisory Committee on Disability Compensation privately recommended to Allison A. Hickey, under secretary for benefits, that the Department of Veterans Affairs consider four steps to address a "recent surge" in VA compensation awards for sleep apnea.
The proposals, which only now come to light, were drafted the same day that committee members received a public briefing on sleep apnea, which confirmed a 25-fold jump in compensation payments since 9/11. The VA briefer also noted that 13 percent of all veterans with service after 9/11 and who draw VA disability pay are being compensated for sleep apnea.
The committee, chaired by retired Army Lt. Gen. James Terry Scott, recommended that VA:
-- Have compensation exams for sleep apnea given exclusively by VA doctors to ensure required sleep tests are properly conducted.
-- Have the Institute of Medicine conduct a detailed study on degree of actual disability associated with sleep apnea, particularly for veterans who are prescribed a CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machine, which under VA regulations results in an automatic rating of 50 percent.
-- Conduct a review of criteria and methodology for establishing service connection to sleep apnea.
-- Review criteria for establishing average earning loss for veterans diagnosed with sleep apnea.
Which of these did VA undertake over the last seven months?
VA officials can't point to any action taken on these recommendations, but said they do inform an ongoing process to overhaul the VA Schedule for Rating Disabilities (VASRD). They may be "redundant of other research associated with the VASRD revision process…. Any recommendations regarding the rating criteria for sleep apnea are still under consideration by the regulation drafter for this body system."
Ratings "assigned for sleep apnea and all other respiratory conditions are being evaluated on an objective basis, using advances in medical science and data from average earnings loss studies," the VA said.
Meanwhile, in fiscal 2013, veterans receiving compensation for sleep apnea jumped by another 26 percent, or more than 29,000 beneficiaries, VA data show. As of Oct. 1, a total of 143,278 vets were rated disabled by sleep apnea, and 89 percent of their ratings were at least 50 percent.
Reached by email, Scott confirmed sending a memorandum to Hickey, which he said, "can be described as an interim report on the issue of sleep apnea," offering advice on behalf of the committee.
"Our advice is based on our understanding of the issue and does not consider the political environment inside or outside VA," Scott said. "The Secretary may act on our advice, refer our advice to the VA staff for study, or reject our advice in whole or in part."
The most common form of sleep apnea is obstructive. It occurs when breathing is interrupted, usually because soft tissue in the back of the throat collapses, blocking the airway. Breathing interruptions, or apneas, can be frequent and last seconds or longer, causing chronic fatigue if untreated.
Incidence of sleep apnea is rising in tandem with obesity rates in this country, say medical experts, although there can be other causes.
The most common path to a VA sleep apnea disability rating, the briefer told the committee, is to be "overweight" and have this common sleep disorder diagnosed as they separate or retire from service.
In revising the VASRD, officials said veterans would be grandfathered against rating downgrades. Any changes would apply only to new claimants. Discussion raises anxieties, however, and also gives rise to new claims.
A 50-percent rating is a key threshold, making retirees eligible to receive both full retirement and VA disability pay, at that rate $822 to $1088 a month, depending on family size. Most retirees rated less than 50 percent see retired pay offset, dollar-for-dollar, by VA disability pay.
Of roughly 29,200 veterans who began receiving sleep apnea compensation in the last year, 93 percent had ratings of 50 percent or higher. So that proportion, already high, appears to be climbing.
By comparison, a soldier who loses two dominant fingers, such as a thumb and index finger, also earns a disability rating of 50 percent.
Michael Webster, a family law attorney in Shalimar, Fla., and former naval aviator, complained to the House Veterans Affairs Committee last year of widespread abuse in sleep apnea claims. He called the boom in payments a scam perpetuated mostly by retirees coached toward an easy 50-percent rating. If they snore, he said, they know to order a sleep study. Webster called it an offensive for veterans, like his late father, with "real disabilities."
Is Under Secretary Hickey concerned about tax dollars being wasted in an explosion of sleep apnea claims?
"It is the position of the Veterans Benefits Administration that it is never a waste of tax dollars to pay veterans the benefits to which they are legally entitled," the VA responded. "Our primary concern is to ensure that veterans, their families and their survivors receive disability compensation to which they are entitled."
A staff member for the House Veterans Affairs Committee investigated Webster's charges and concluded "there does not appear to be widespread abuse of compensation related to this disorder."
His report is silent on the larger issues raised by VA advisors -- whether obstructive sleep apnea is disabling when a CPAP is prescribed and provides relief, and whether CPAP usage should trigger a 50-percent rating. As reported here last year, VA's own top expert on sleep apnea said if a CPAP gives its user a good night's sleep, there probably is no disability.
"Many people who have sleep apnea and are on treatment are not disabled. I would say the majority," said Dr. Samuel Kuna, chief of sleep medicine at the Philadelphia VA Medical Center.
VA didn't compensate for sleep apnea before 1996. In 2013, VA apnea payments likely totaled between $1.5 billion to $2 billion a year.
Send comments to Military Update, P.O. Box 231111, Centreville, VA, 20120, email milupdate@aol.comor twitter: Tom Philpott @Military_Update